
BY :CHAIMAE ILLI
INTRODUCTION
TO
DATA
ANALYSIS

a Data Science and
Business Intelligence
student at the Cadi Ayyad
university and the Event
Manager of the SDAD club
This course is done by:
ILLI
Chaimae
https://www.linkedin.com/in/chaimae-illi-265215209
chaimae.rema@gmail.com

Overview:
Introduction
What is data analysis?
Uses of Data analysis
Data analysis tools
Data analysis process
Data analysis types
Why is data analysis important?

Today we collect data at various
points of processes and
transactions, which has huge
potential to change the way we
work for the better. However, this
data analysis can add value to the
business only when it’s analyzed to
gain insights into how to improve
your products and services.
Data analysis allows you to know
and interpret information to identify
points of value. But what is data
analysis in simple words?
What is data analysis?
Data analysis is the science of examining a
set of data to draw conclusions about the
information to be able to make decisions or
simply to expand the knowledge on various
subjects.

Data Analysis is one of the most important
processes that businesses can leverage to make
the right decisions.
Effective data analysis is a skill that can be applied
to finance, retail business, medicine, and
healthcare, and even in the world of sports
Why is data analysis important ?
Uses of data analysis:
It is used in many industries regardless of the
branch. It gives us the basis to make decisions or
confirm if a hypothesis is true:

Mainly, researchers perform
data analysis to predict
consumer behavior and help
companies place their
products and services in the
market accordingly.
Universities and academic
institutions can perform
data analysis to measure
student performance and
gain insights into ways
education can be further
improved.
Marketing : Academics:
Organizations can use data
analysis to offer a great
experience to their
employees and ensure an
excellent work environment.
They can also utilize the
data at hand to find out the
best resources – the ones
whose skill set matches with
the organizational goals.
Human Ressources:

Data analysis tools:
In order to perform high-quality data analysis,
it is fundamental to use tools and softwares that will ensure the best results. As the analysis industry grows, so
does the offer for services and features that you can exploit

Data analysis process:
As the data companies have available to them continues to
grow in both amount and complexity, so does the need for
an effective and efficient process by which to harness the
value of that data. The analysis method typically moves
through several iterative phases. Let’s take a closer look at
each.
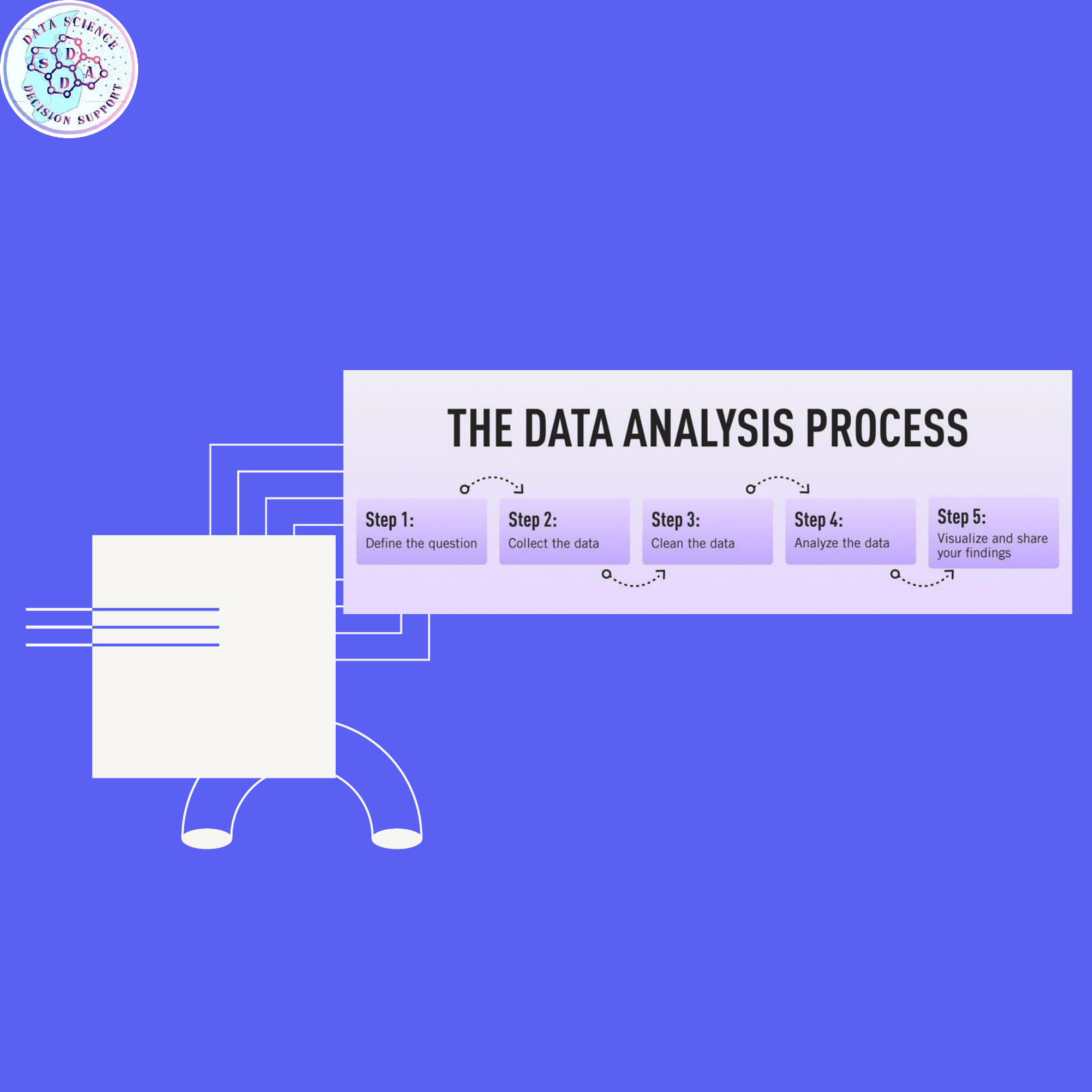

Data Requirement Gathering
Ask yourself why you’re doing this
analysis, what type of data analysis you
want to use, and what data you are
planning on analyzing.
Data Collection :
Guided by the requirements you’ve
identified, it’s time to collect the data from
your sources. Sources include case
studies, surveys, interviews,
questionnaires, direct observation, and
focus groups. Make sure to organize the
collected data for analysis.

Data Cleaning :
Not all of the data you collect will be
useful, so it’s time to clean it up. This
process is where you remove white
spaces, duplicate records, and basic
errors. Data cleaning is mandatory before
sending the information on for analysis.

Data Analysis:
Here is where you use data analysis
software and other tools to help you
interpret and understand the data and
arrive at conclusions. Data analysis tools
include Excel, Python, R, Looker, Rapid
Miner, Chartio, Metabase, Redash, and
Microsoft Power BI.

Data Interpretation :
Now that you have your results, you need
to interpret them and come up with the
best courses of action, based on your
findings.

Data Visualization :
Data visualization is a fancy way of
saying, “graphically show your information
in a way that people can read and
understand it.” You can use charts, graphs,
maps, bullet points, or a host of other
methods. Visualization helps you derive
valuable insights by helping you compare
datasets and observe relationships.
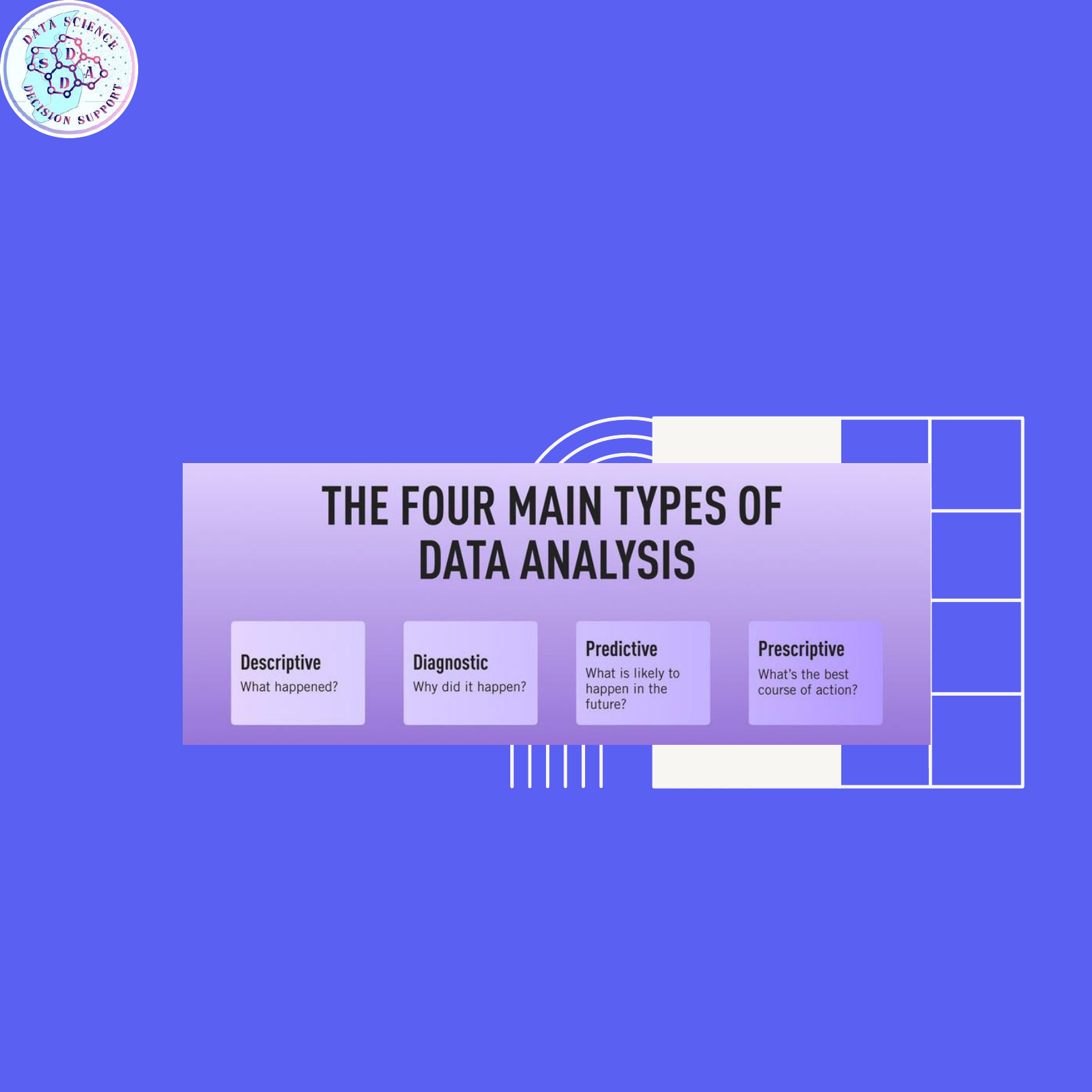
Types of Data Analysis:

Descriptive Analysis : works with either
complete or selections of summarized
numerical data. It illustrates means and
deviations in continuous data and
percentages and frequencies in categorical
data.

• Diagnostic Analysis: Diagnostic analysis
answers the question, “Why did this
happen?” Using insights gained from
descriptive analysis . analysts use
diagnostic analysis to identify patterns in
data. Ideally, the analysts find similar
patterns that existed in the past, and
consequently, use those solutions to
resolve the present challenges hopefully.

• Predictive Analysis: Predictive analysis
answers the question, “What is most
likely to happen?” By using patterns
found in older data as well as current
events, analysts predict future events.
While there’s no such thing as 100
percent accurate forecasting, the odds
improve if the analysts have plenty of
detailed information and the discipline to
research it thoroughly.

• Prescriptive Analysis: Mix all the
insights gained from the other data
analysis types, and you have prescriptive
analysis. Sometimes, an issue can’t be
solved solely with one analysis type, and
instead requires multiple insights.
Conclusion:
Data analysis has multiple facets and approaches,
encompassing diverse techniques under a variety of
names, and is used in different business, science, and
social science domains. In today's business world,
data analysis plays a role in making decisions more
scientific and helping businesses operate more
effectively
Thank you!
BY: ILLI CHAIMAE
Club SDAD
sdad.club22@gmail.com
club_sdad
Club SDAD
Contact Us